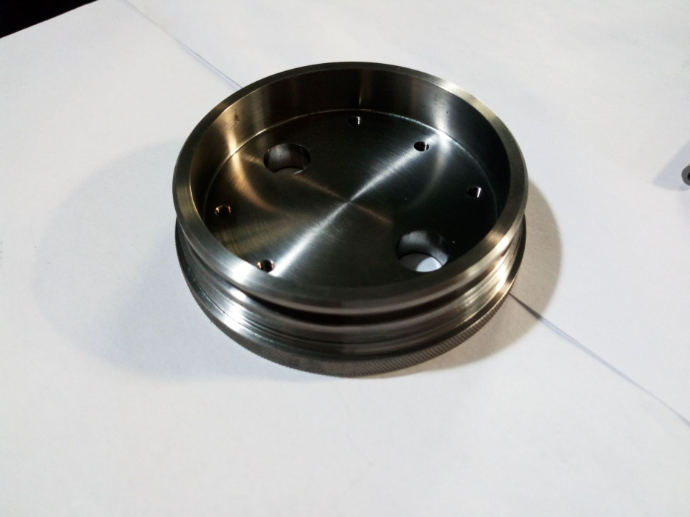
Titanium
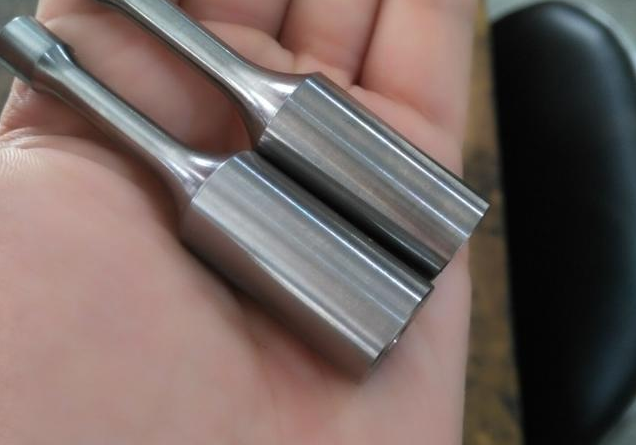
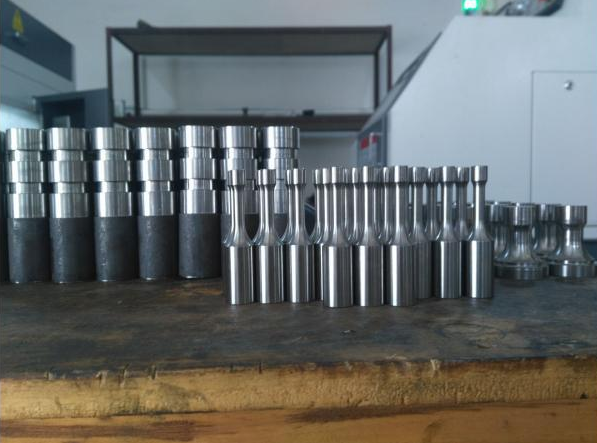
Titanium metal looks like steel, has a silver-gray luster and is a transition metal. Titanium has high strength, low density, high hardness, high melting point and strong corrosion resistance; high-purity titanium has good plasticity, but becomes brittle and hard when impurities are present.
Ideal for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries.It is corrosion-resistant (including to salt water) and resists tarnishing at room temeratures. Titanium is ductile and has a high melting point. Though it is more than 60% heavier than aluminum it is more than twice as strong as 6061-T6.
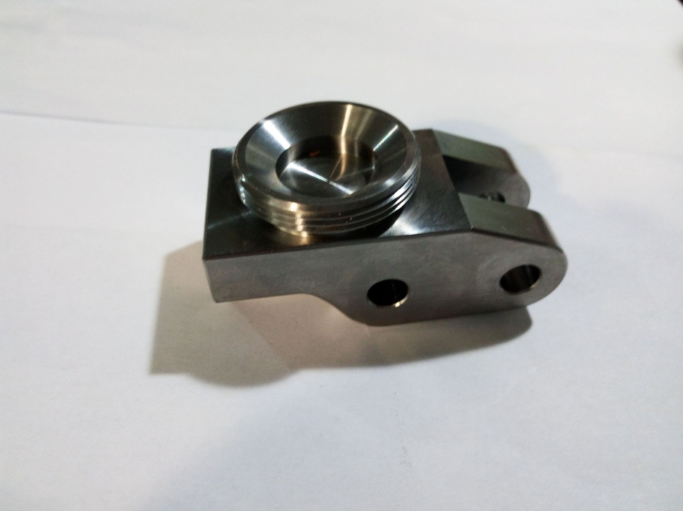
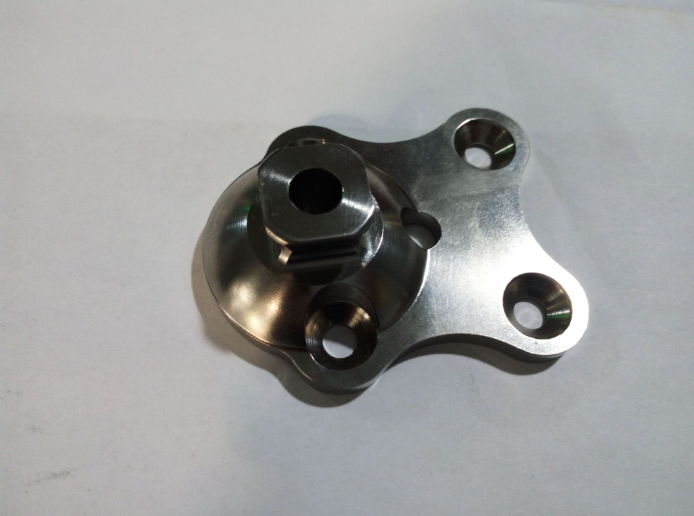
Titanium is often used in: jet engines, missiles, spacecraft, medical prostheses, orthopedic implants, medical instruments, sporting goods, landing gear, hydraulic systems, aircraft frames, rotors, compressor blades, hydraulic system components, propeller shafts, ocean-deployed surveillance and monitoring devices, submarines, heat exchangers, tanks, chemical process vessels, valves, auto and motorcycle racing, hammer heads, tennis rackets, golf clubs, football helmet grills, bicycle frames and components, spectacle frames, forged titanium fans, compressor discs and blades, bearing housings, etc. The spacecraft mainly utilizes the high specific strength, corrosion resistance and low temperature resistance of titanium alloys to manufacture various pressure vessels, fuel tanks, fasteners, instrument straps.Titanium alloy plate welded parts are also used in artificial earth satellites, lunar modules, manned spacecraft and space shuttles.engagement rings, wedding bands, watch cases, body piercing, sculptures and furniture.